As mentioned earlier, companies are expected to realize “social value” in their activities. This “social value” can be more specifically considered from the perspectives of “CSV” and “CSR.”
CSV stands for Creating Shared Value. In other words, it means creating both economic value that benefits the company and social value that benefits society. A typical example of something that benefits a company (i.e., an organization or group) but does not benefit society is activities carried out by anti-social groups (i.e., criminal activities). Such activities may be profitable for those groups but are harmful to society, meaning they do not create social value.
In addition to CSV, which refers to generating both economic value and social value, the concept of CSR is also important. CSR stands for Corporate Social Responsibility. The responsibility here refers to “good deeds” that do not generate economic value for the company. An example would be volunteer activities carried out by the company.
Activities of a company to realize CSV and CSR:
CSV (economic value + social value) and CSR (social responsibility) that companies should realize can be broadly classified into “Offensive Activities” and “Defensive Activities,” and can be categorized into four types as shown in the diagram below.
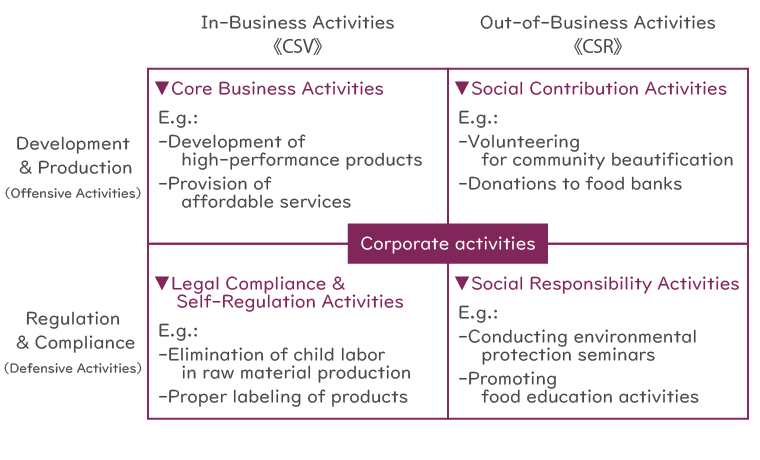
Companies are expected to exist to solve social issues and create social value. While competition with other companies is inevitable in aiming for growth in society, it is not necessarily correct to focus solely on defeating competitors and eliminating them from the market. The increase in competitors in society (i.e., the market) leads to an increase in consumers, the expansion of the market size, and a greater impact on government agencies and authorities. These changes result in the creation of even more social value, which is enjoyed by more people. If there were only one company in the market, consumers would be forced to buy services or products at exorbitant prices if that company set such prices. This would be a great misfortune for consumers.
To ensure the healthy development of a company, it is important to engage a wide range of stakeholders. This includes not only employees, but also suppliers of raw materials, manufacturers, logistics providers, distributors, and even consumers. By creating relationships with many stakeholders and forming a cluster centered around the company, this becomes the path for the company’s growth.

No comments yet.